Drawing Of Dna Replication
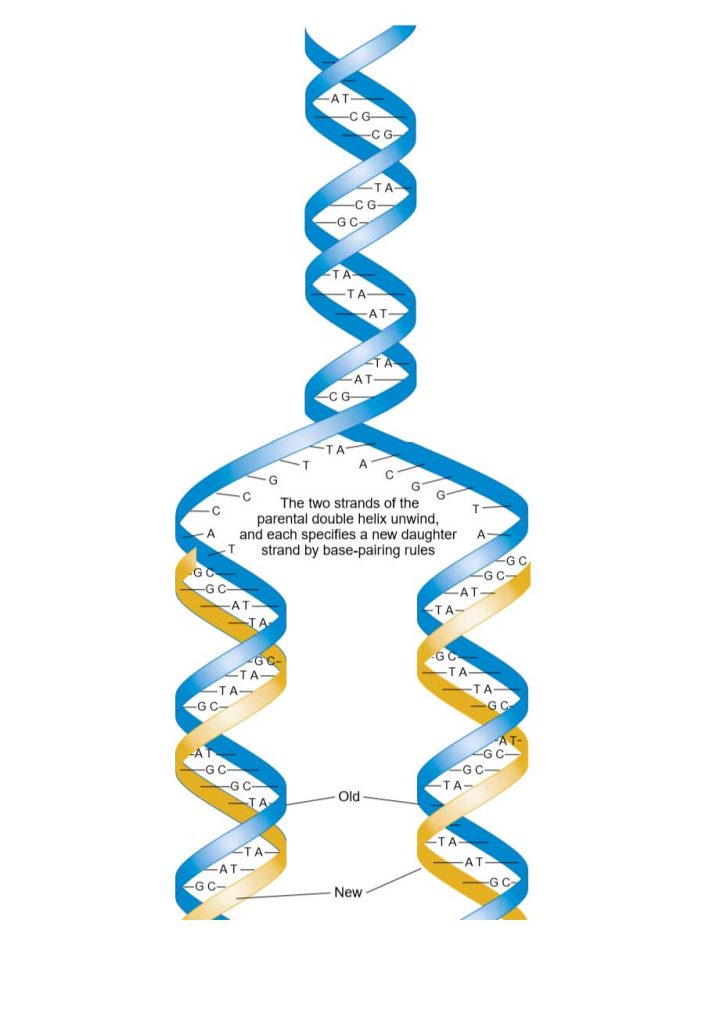
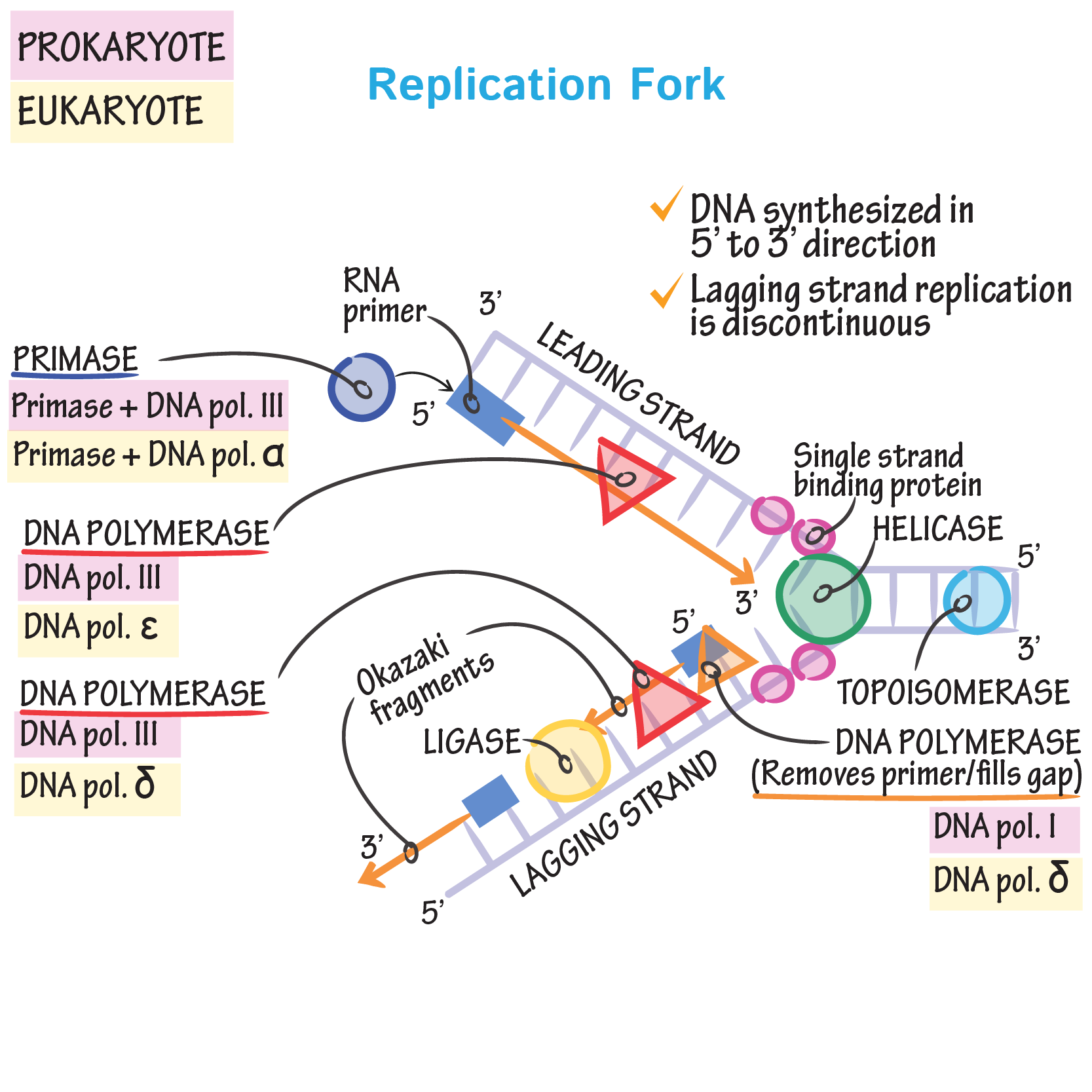
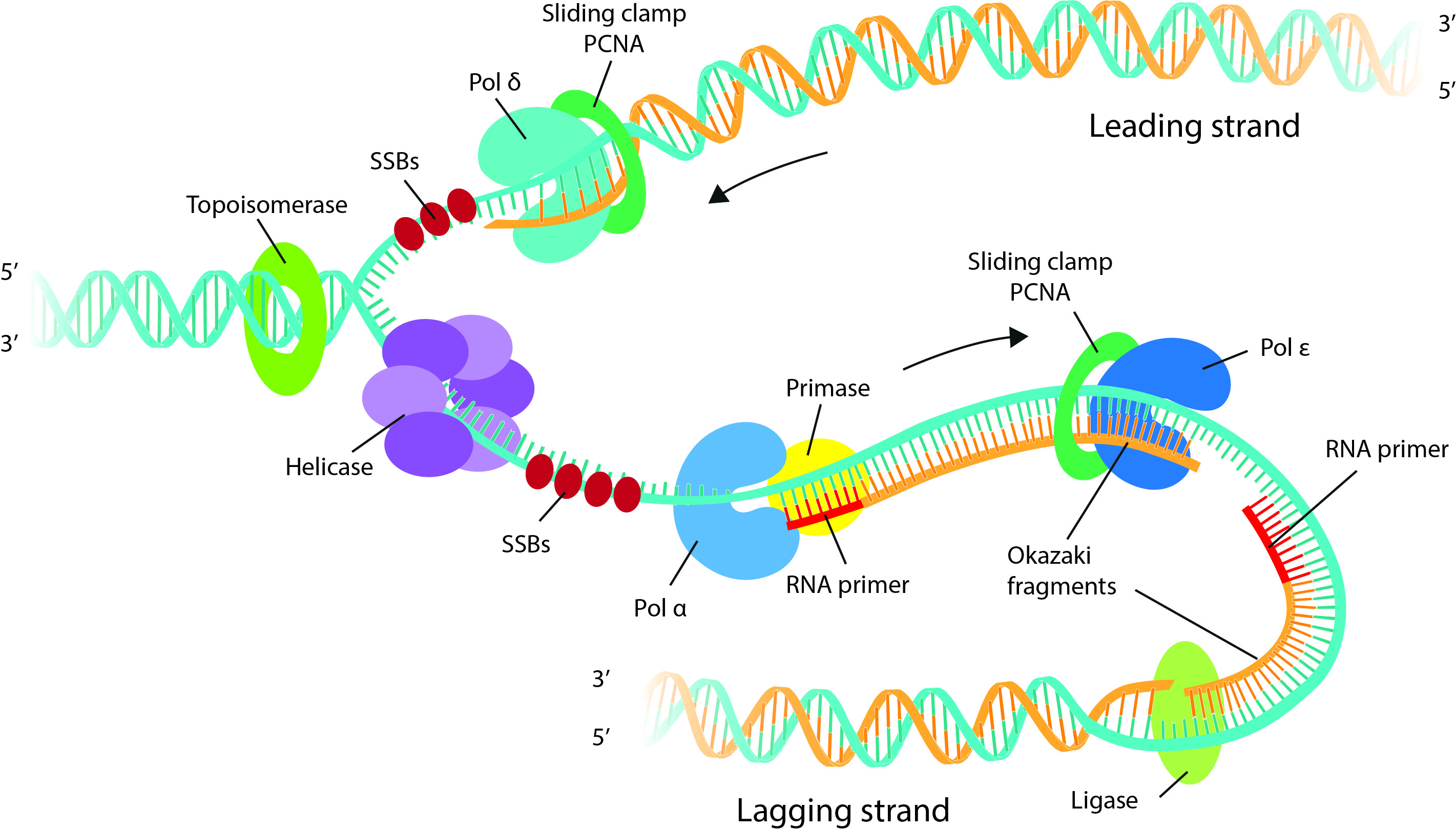
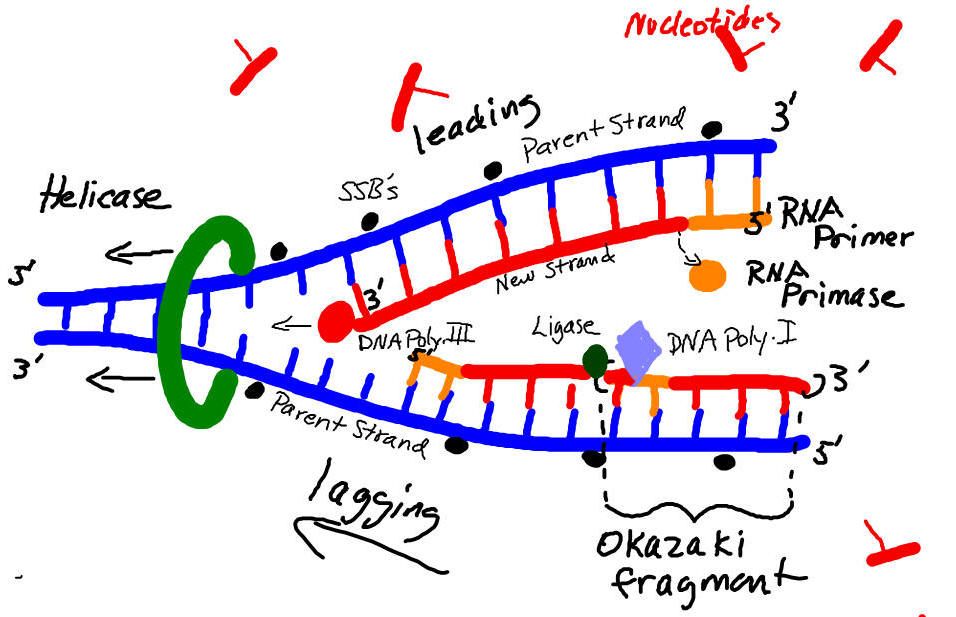
Drawing Of Dna Replication - In this article, we shall discuss the structure of dna, the steps involved in dna replication (initiation, elongation and termination) and the clinical consequences that. Web as previously mentioned, the location at which a dna strand begins to unwind into two separate single strands is known as the origin of replication.as shown in figure 1, when the double helix. A replication fork is formed by the opening of the origin of replication, and helicase separates the dna strands.an rna primer is synthesized, and is elongated by the dna polymerase. Why is dna replication such an important process. Each molecule consists of a strand from the original molecule and a newly formed strand. A replication fork is formed which serves as a template for replication. Half of the parent dna molecule is conserved in each of the two daughter dna molecules. Web the replication fork is the branched (forked) dna at either end of the replication bubble. Thus, replication cannot initiate randomly at any point in dna. So, as your cells divide, they would have a different dna. This is the point where the replication originates. This imaginary polymerase that elongates the 5' end of the growing chain. A replication fork is formed which serves as a template for replication. Half of the parent dna molecule is conserved in each of the two daughter dna molecules. Web during dna replication, each of the two strands that make up the double helix serves as a template from which new strands are copied. However, the procedure is the same in humans and other eukaryotes. Web before we jump into the process of replication, let us take a quick look at the structure of dna. Each molecule consists of a strand from the original molecule and a newly formed strand. A nucleotide, in turn, is made up of phosphate molecule, deoxyribose, and a nitrogenous base. For the replication to begin there is a particular region called the origin of replication. So, as your cells divide, they would have a different dna. Each molecule consists of a strand from the original molecule and a newly formed strand. A plasmid with an origin of replication (ori) is a replication unit. Web during dna replication, each of the two strands that make up the double helix serves as a template from which new. For example, say you had a portion of your genome. So, as your cells divide, they would have a different dna. This is the point where the replication originates. Where one has a g, the other has a c; As we have seen, dna synthesis starts at one or more origins or replication. Try drawing this situation, for a real polymerase vs. As we have seen, dna synthesis starts at one or more origins or replication. Each molecule consists of a strand from the original molecule and a newly formed strand. However, the procedure is the same in humans and other eukaryotes. In dna replication, you could get two completely different strands of. This is the point where the replication originates. Why is dna replication such an important process. These are dna sequences targeted by initiator proteins in e. A replication unit is any chunk of dna that is capable of being replicated — e.g. On the leading strand, dna is synthesized continuously, whereas on the lagging strand, dna is. Web some other proteins and enzymes, in addition the main ones above, are needed to keep dna replication running smoothly. Why is dna replication such an important process. These are dna sequences targeted by initiator proteins in e. This model made a lot of sense given the structure of the dna double helix, in which the two dna strands are. Web the replication fork is the branched (forked) dna at either end of the replication bubble. Web dna replication demands a high degree of accuracy because even a minute mistake would result in mutations. Web learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. As we all know, dna is the genetic. A replication fork is formed by the opening of the origin of replication, and helicase separates the dna strands.an rna primer is synthesized, and is elongated by the dna polymerase. Try drawing this situation, for a real polymerase vs. In dna replication, you could get two completely different strands of dna than what you started with. For example, say you. This is the point where the replication originates. So, as your cells divide, they would have a different dna. The double helix unwinds and each strand acts as a template for the construction of the new dna molecule. Web learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. For example, say you. The double helix unwinds and each strand acts as a template for the construction of the new dna molecule. Try drawing this situation, for a real polymerase vs. Web during dna replication, each of the two strands that make up the double helix serves as a template from which new strands are copied. Nucleotides that compose dna are called deoxyribonucleotides.. One strand runs from 5′ to 3′ direction towards the replication fork and is referred to as leading strand and the other strand runs from 3′ to 5′ away from the replication fork and is referred to as lagging strands.; Web formation of replication fork step 2: Web the replication fork is the branched (forked) dna at either end of. The replication complex is the group of proteins that help synthesize the new dna strands. A replication unit is any chunk of dna that is capable of being replicated — e.g. And so forth) 2, 4 . Thus, replication cannot initiate randomly at any point in dna. Web this animation shows a schematic representation of the mechanism of dna replication. A nucleotide, in turn, is made up of phosphate molecule, deoxyribose, and a nitrogenous base. This is the point where the replication originates. For example, say you had a portion of your genome. Where one has a g, the other has a c; Figure 5.4.4 the two strands of nucleotides that make up dna run antiparallel to one another. The building blocks of nucleic acids are nucleotides. Web here, we will focus on dna replication as it takes place in the bacterium e. Web learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. As we have seen, dna synthesis starts at one or more origins or replication. So, as your cells divide, they would have a different dna. Web dna is a double helix structure comprised of nucleotides.DNA Replication Study Solutions
Dna Replication Drawing at Explore collection of
Diagram Of Dna Biology Labelled Replication Label Digital Art By Images
Dna Replication Drawing at GetDrawings Free download
DNA Replication Lagging Strand
DNA Replication — Steps & Diagram Expii
DNA Replication Microbiology
Dna Replication Drawing at Explore collection of
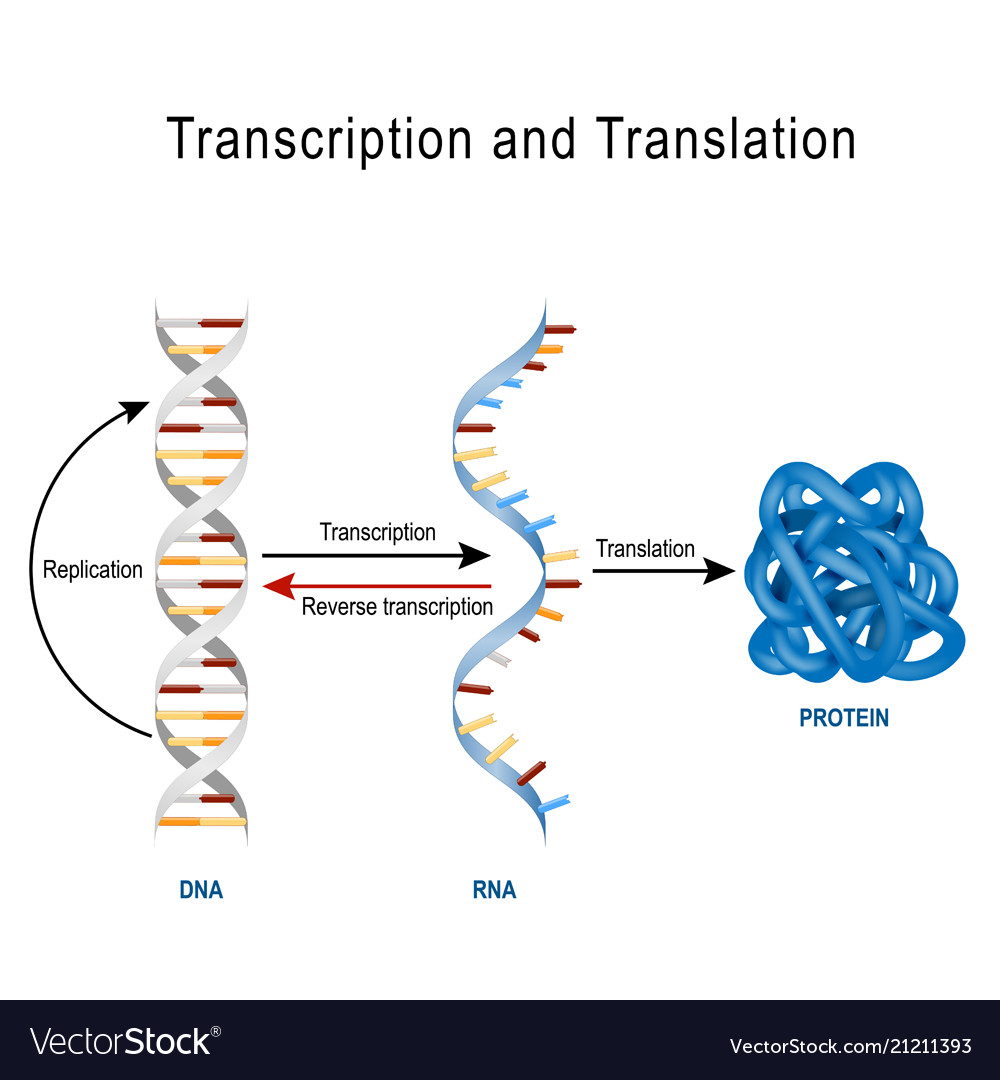
Dna replication protein synthesis transcription Vector Image
Dna Replication Diagram With Labels
Web Before We Jump Into The Process Of Replication, Let Us Take A Quick Look At The Structure Of Dna.
Therefore, If The First Strand Starts At The 3′ End And Finishes At The 5′ End, Then The Second Strand Must Run Opposite, Starting At The 5′ End And.
Why Is Dna Replication Such An Important Process.
Web The Replication Fork Is The Branched (Forked) Dna At Either End Of The Replication Bubble.
Related Post: